Solid-State Drives (SSDs) are a popular modern storage device used in computers that store data with flash-based memory. It is significantly faster than the traditional hard disks that it is replacing. Additionally, SSDs have no moving parts, which enhances their durability.
Yes, they are better than hard drives, but data loss can happen anytime, no matter how supreme your SSD is.
According to Google, an average of 5000 people all over the world search for the keyword SSD recovery every month. A study by Backblaze found that SSDs have a higher annual failure/corruption rate than HDDs, with some models experiencing failure rates as high as 13%. Shocking.
So, if you are in a similar situation where you lost valuable data from your SSD drive, don't worry. This article has everything you need to know about SSD data recovery.
But before we proceed to the recovery process, let's find out some interesting facts about SSDs that can help you understand everything about them and perform hassle-free SSD recovery.
Want to skip the introduction and jump straight to the SSD data recovery part? Click here.
- How SSD Works?
- Functionality and Benefits of Solid-State Drive
- From SATA to PCIe: Exploring the Various Types of Solid-State Drives
- What's the difference between SSDs and HDDs?
- Is It Possible to Recover Data From SSD?
- How to Recover Data From SSD?
- Common Indicators of SSD Corruption and Failure
- Frequently Asked Questions
How SSD Works?
An SSD stores data in NAND flash memory and uses a controller to manage the data. The controller decides where data should be stored and retrieves it when needed. It also addresses the cache, a small amount of memory that temporarily stores frequently accessed data for faster access. The controller's role is essential in ensuring quick and efficient access to data on the drive.
Here are the components of an SSD:
The Components of an SSD
1. NAND Flash Memory: This is like the long-term memory of the SSD. It's where all your data is stored, even when the power is turned off. The cells in this memory can store lots of bits of data each, allowing lots of data to be stored in a small space.
2. Controller: The controller is like the conductor of an orchestra. It manages the data flow between your computer and the NAND flash memory, ensuring everything runs smoothly. It also ensures that data is written evenly across the cells, so the memory wears out evenly over time.
3. Cache: The cache is like the short-term memory of the SSD. A small amount of high-speed memory acts as a middleman between your computer and the NAND flash memory. When you access data frequently, the cache stores it temporarily to be accessed quickly, speeding up your computer's performance.
Functionality and Benefits of Solid-State Drive
Most new computers now use SSDs for storing information because they are faster, smaller, and lighter than older HDDs.
SSDs work like a super-fast digital filing cabinet, allowing your computer to access your files quickly. They used to be expensive, but they are common in everyday computers because they offer a better user experience.
SSDs offer distinct advantages in the following areas:
- Gaming: Gaming computers need fast storage to load games quickly, and SSDs offer the speed gamers demand. New gaming consoles, like the PS5 and Xbox Series X, have also switched to SSDs for better gaming performance.
- Mobility: SSDs are ideal for mobile devices like laptops and tablets because they require less power than HDDs, which means longer battery life. They're also shock-resistant, so your data is less likely to be lost if you accidentally drop your device.
- Servers: Enterprise servers need fast read and write times to quickly serve data to client computers. SSDs offer the speed required to ensure that clients can access data as soon as possible
- Faster boot times: Computers with SSDs can boot up much faster than those with HDDs.
- Better performance: Applications load and run more quickly on SSDs, which can improve overall system performance.
- Smaller size and weight: SSDs are much smaller and lighter than HDDs, making them ideal for small devices like ultrabooks and tablets.
- Less heat and noise: SSDs generate less heat and noise than HDDs, which can improve the overall user experience.
From SATA to PCIe: Exploring the Various Types of Solid-State Drives
You know the functionality and benefits of Solid-State Drives now. But do you know many types of SSDs available in the market? Of course, it's crucial to understand each SSD type to recover data from SSD.
- SATA SSD: These SSDs are the most common and affordable type of SSD, but the SATA interface limits them and offers slower speeds compared to other types. However, data loss is still a common risk due to accidental deletion, hardware failure, or malware. Refer to our article to recover data from SATA hard drives/SSDs.
- NVMe SSD: NVMe SSDs use the PCIe interface and offer faster speeds and better performance than SATA SSDs. NVme SSDs are indeed better SSDs and are used widely, but data loss is close to such SSDs. If you want to recover data from NVme SSDs, refer to our in-depth article on how to recover data from NVMe SSD.
Interesting Read: Find out Why you should upgrade SATA SSD to NVMe?
- M.2 SSD: These SSDs are small and compact, making them ideal for laptops and other small devices. They can use the SATA or NVMe interface, but data loss is still risky.
- U.2 SSD: U.2 SSDs use the NVMe interface and are primarily used in high-end workstations and servers. They offer fast speeds and low latency but are less common and more expensive than other types of SSDs.
- PCIe SSD: These SSDs use the PCIe interface and offer the fastest speeds and lowest latency of any SSD type. These SSDs are very expensive.
What are SSD form factors?
SSD form factors refer to solid-state drives' different physical shapes and sizes. Below we have mentioned all SSD form factors:
1) 2.5" Form Factor
This is the most common type of SSD and is compatible with most laptop and desktop computers. It has a similar shape to a traditional hard disk drive (HDD) and connects over SATA cables, providing a familiar experience to users.
2) M.2 Form Factor
This tiny form factor has become the standard type of storage for slim laptops and notebooks.
It is often compared to a stick of gum and can be installed directly on the motherboard in most cases. In addition, it is available in different lengths to enable various SSD drive capacities.
3) mSATA Form Factor
This smaller version of the full-size SATA SSD uses a compact form factor like M.2. However, it is not interchangeable.
M.2 drives can support both SATA and PCIe interface options, while mSATA only supports SATA. This form factor is designed for smaller form factor systems where space is limited.
4) U.2 Form Factor
This looks like a 2.5" drive but is a bit thicker. It uses a different connector and sends data through the PCIe interface.
U.2 SSD technology is typically reserved for high-end workstations, servers, and enterprise applications that need greater storage. It allows higher operating temperatures and is more favorable for transferring heat than the M.2 form factor.
What's the difference between SSDs and HDDs?
If you are wondering about the differences between a Hard Disk Drive and a Solid-State Drive, refer to this helpful table.
| SSDs | HDDs | |
| Speed | Faster | Slower |
| Lifespan | Shorter | Longer |
| Cost | More expensive | Cheaper |
| Noise | Silent (no moving parts) | Audible clicking and spinning noise |
| Fragility | More durable (no moving parts) | More susceptible to physical damage and data loss due to mechanical failure |
| Energy consumption | Lower power consumption | Higher power consumption |
| Heat generation | Produce less heat | Can produce more heat due to moving parts |
| Capacity | Typically lower capacity, but increasing rapidly | Higher capacity, but plateauing |
| Access time | Near-instant access to data | Slightly slower access time |
| Shock resistance | More resistant to shocks and vibrations | Less resistant to shocks and vibrations |
| Weight | Lighter weight | Heavier weight |
Is It Possible to Recover Data From SSD?
Yes, it is possible to recover data from SSD, but it is very challenging compared to data recovery from hard drives.
Unlike HDDs, which use spinning disks and magnetic heads to read and write data, SSDs utilize flash memory chips to store data electronically. This technology offers several advantages, such as faster access times and increased reliability. However, it also presents specific challenges when it comes to data recovery:
- Wear leveling: SSDs use wear leveling algorithms to distribute data across memory cells evenly. This means that the data is spread across multiple locations on the drive instead of being stored consistently. Wear alignment can help extend the life of SSDs, but it can make data recovery more complicated because the location of the data cannot be mapped directly.
- TRIM command: SSDs use the TRIM command to improve performance and extend the drive's life. When files are deleted or overwritten, the TRIM command tells the SSD to mark those blocks as reusable. As a result, deleted data is quickly erased from the drive and is more difficult to recover.
- Write operation limitations: SSDs limit the number of write cycles per memory cell. Since cells are written repeatedly, they can become corrupted over time and lead to data loss. If the SSD cells are severely degraded, recovery becomes more difficult because the damaged cells may not retain the original data.
- Encryption: Many modern SSDs support hardware-level encryption for added security. While this feature protects your data in the event of theft or unauthorized access, it also increases the complexity of data recovery efforts. If the encryption key is unavailable, recovering data from an encrypted SSD becomes tough.
Even though it is possible to recover data from SSD, the process can be challenging depending on the data loss scenario and the factors mentioned above.
To recover deleted files from SSD, you need specialized tools, expertise, and, in the worst cases, professional data recovery services.
How to Increase Chances of Successful SSD Recovery?
From the above section of this article, we know that SSD recovery can be challenging, but it is possible. To increase the chances of successful SSD data recovery, it is essential to be extra careful and follow the steps below to perform hassle-free data recovery from SSD:
Disconnect the SSD immediately.
If you find some critical data or files missing from your SSD drive, we recommend quickly shutting down your computer and removing the SSD drive. Then, by turning it into an external drive and connecting it to another computer, you can perform the recovery process. Unfortunately, if the SSD is left in that PC and the PC is restarted, the TRIM command will run automatically (if enabled), making data recovery very difficult.
Select the best SSD recovery software.
Regarding SSD data recovery, it is essential to use a reliable and professional tool to ensure the successful retrieval of lost data. Therefore, we highly recommend using Remo Recover, a powerful SSD recovery software that can quickly recover data from corrupted, dead, or failed SSD.
Additionally, Remo Recover can recover lost partitions from SSDs, making it a comprehensive solution for SSD data recovery.
Note: Discover the top 5 SSD recovery tools of 2023 by reading our expert review on the best SSD recovery tool, which comprehensively analyzes each tool's capabilities.
Disable the TRIM command.
We recommend disabling the TRIM command if you have only one system and your primary drive is an SSD. Then, if you lose data on your SSD drive, you don't have to rush to recover it. Instead, start looking for someone to lend you a PC so you can use it for recovery.
Here are the steps to Disable TRIM on Windows 11, 10, 8, and 7:
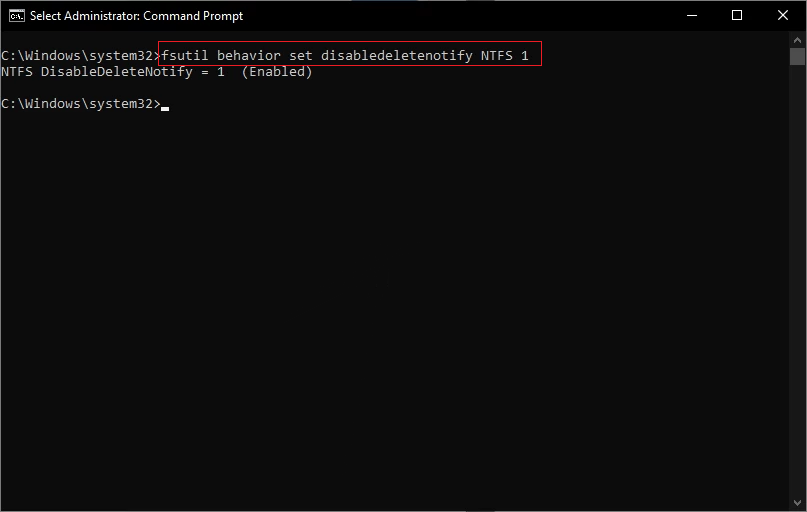
Step 1: Type cmd in the start menu.
Step 2: Right-click on the cmd suggestion and select Run as Administrator.
Step 3: once the Administrator command prompt is open, type the command: "fsutil behavior set DisableDeleteNotify=1" and hit Enter.
Now you have seen all the aspects of SSD and are all set to recover data from SSD. So without wasting any more time, let's recover deleted data from the SSD.
How to Recover Data From SSD?
Below we have mentioned two effective methods to help you recover data from SSD.
Method 1: Recover Deleted Data From SSD Using SSD Recovery Software
You need a professional SSD recovery tool like Remo Recover to recover data from SSD.
Remo Recover is an excellent solution for recovering data from formatted SSD drives. Its advanced scanning algorithms and powerful recovery features make it an effective tool for recovering lost, deleted, or formatted data from various types and brands of SSD drives, such as Samsung, Kingston, SanDisk, and others.
With Remo Recover, you can even recover lost data from formatted SSDs quickly and easily. The software supports all major file formats and ensures that you can recover all types of files, including photos, videos, music files, and documents. In addition, its user-friendly interface and step-by-step recovery process make it easy to use even for non-technical users.
Download this tool now and follow the below simple steps to recover permanently deleted files from SSD.
Steps to Recover Data From SSD Using Remo Recover
Time needed: 2 hours and 29 minutes
Here are the simple steps to recover data from SSD using Remo Recover
- Download and Install Remo Recover
Begin by downloading and installing the Remo Recover Windows software on your computer.
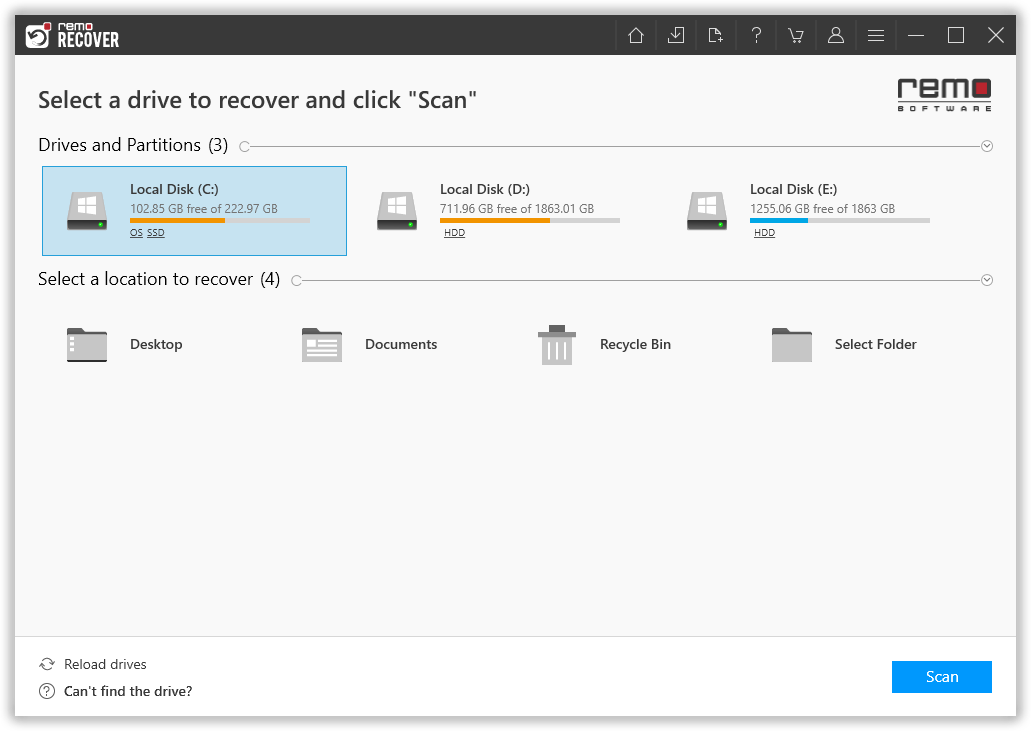
- Launch the tool and select your SSD
Connect the SSD to your Windows computer using a suitable USB cable. First, ensure that the device is connected correctly and detected by the computer. Now, launch Remo Recover Windows and select the SSD from the list of available devices on the home screen.
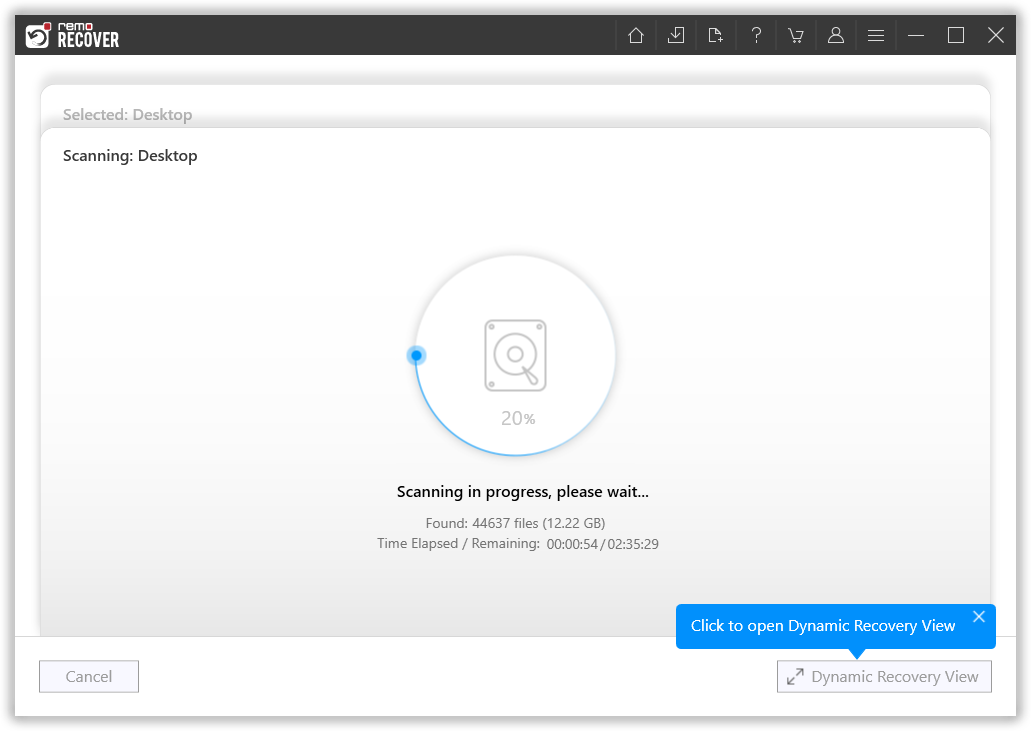
- Scan Your SSD
Click on the Scan button to start the scanning process. Remo Recover will analyze your SSD and attempt to retrieve your lost data.
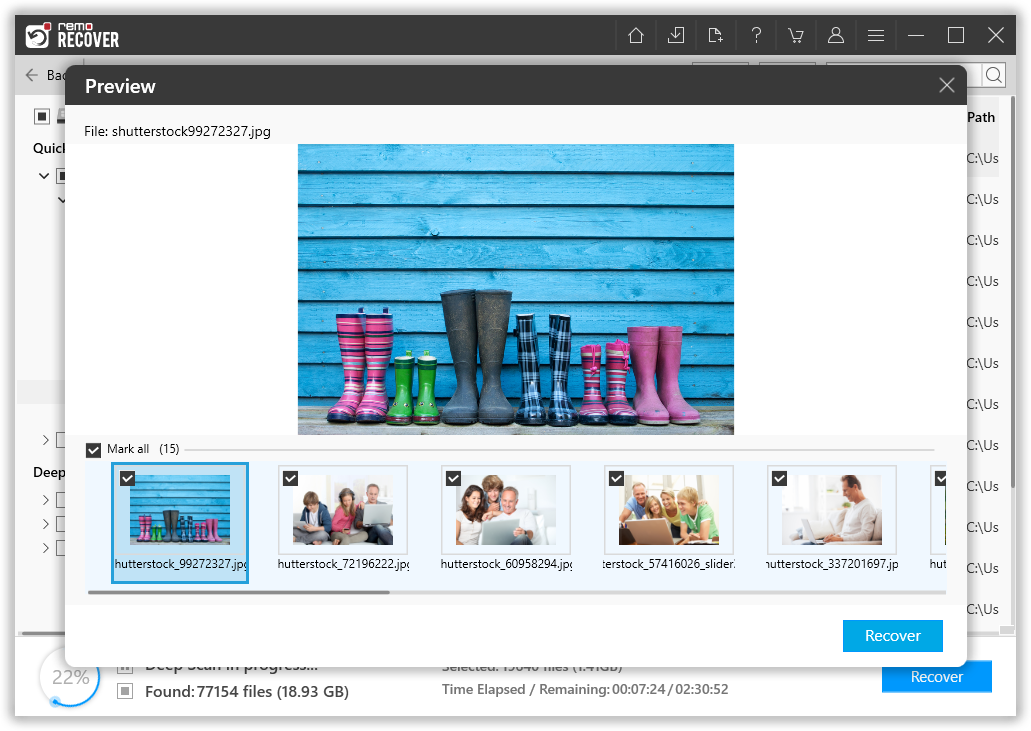
- Preview the Recovered Files
While the scanning is in progress, you can preview the recovered files using the Dynamic Recovery View feature. This will allow you to see the files that have been recovered so far and select the ones you want to retrieve.
- Save the Recovered Files
Once the scanning process is complete, you can preview the recovered files using the Preview feature. Select the files you want to recover and click on the Recover button. Choose a safe location where you want to save the recovered files and click OK to complete the recovery process.
Note: When recovering files from a failing SSD drive, it is crucial to recover them onto a different drive. However, if you are only recovering deleted files from a functioning drive, you can restore them to the same drive.
SSD Data Recovery | A Video Tutorial for Beginners
Method 2: Recover Corrupted/Failed SSD Using Data Recovery Services
In worst-case scenarios, such as severe corruption, damage, SSD not showing up, and failed SSDs, it is possible that no SSD recovery tool, no matter how good it is, will be able to detect your SSD. In such cases, the only option left to you would be to consult a professional data recovery service. These services possess all the necessary equipment which may be able to recover your SSD.
Here are the factors which you need to consider before sending your SSD for repair and recovery for a smooth SSD repair/recovery service:
- ISO certification for their service center
- Utilization of Class 100 clean room
- Guarantee of data recovery after a thorough analysis
- A secure and dependable service
- Complete confidentiality of the retrieved data
- Implementation of a "no recovery, no charge" policy
- Free shipping of the SSD for recovery purposes.
Common Indicators of SSD Corruption and Failure
It's very important to understand the Architecture and Indications of SSD's Failure to keep your SSD safe from unwanted data loss. Here are some common reasons why your SSD might fail.
- Power outages: SSDs require a capacitor and power supplies that are prone to failure: especially in the event of power surges or outages. Power outages also cause the SSD to corrupt existing data, even if the drive has failed.
- Limited read/write cycles: SSDs can potentially pose a problem due to their limited read/write cycles, which is a common issue with all types of flash memory. One specific problem that may arise is a disk write error while using applications like Steam, but you can refer to this article to fix the Steam disk write error on SSD.
- Very slow read/write speed: This clearly indicates SSD failure. The SSD may be damaged or corrupted if the read/write rate is abnormally low.
- Bad Blocks: Like hard drives have "bad sectors," SSDs have "bad blocks." We usually see scenarios where our computer tries to read or save a file, but it takes a long time and fails. The system finally gives up with an error message.
- Frequent crashes during boot: If your computer crashes during the boot process but works fine after pressing the reset button a few times, the drive may be to blame. It's best to back up your data before you lose it, as it could be a sign of bad blocks or drive failure.
- SSD not detected: Another issue you might encounter is when your SSD is not being detected in the BIOS. This problem can have various causes, including a loose connection or outdated drivers. First, try checking the connections to ensure they're secure. If that doesn't work, try updating your SSD drivers or the BIOS itself. If none of these solutions work, it may be necessary to replace the SSD entirely.
Ensure you always take a backup of your computer on an external hard drive/SSD or any other storage device to keep your data safe.
Frequently Asked Questions
To recover data from formatted SSD first download and install Remo Recover on your system and follow the below steps:
1.) Connect your Formatted SSD to the computer.
2.) Now, Launch the software on your system, select the formatted SSD drive from the home menu and click on the Scan option.
3.) After completion of the scanning process, a list of recovered files is displayed under the Lost and Found folder or Lost Partition folder.
4.) You can preview all the recovered files using the Preview feature for free.
5.) If you are satisfied with the recovery results, select the files which you want to restore and hit the Recover button to save them at your desired location.
Yes as compared to HDDs it is harder to recover data from SSDs. SSD drive recovery depends greatly on whether the TRIM command is enabled or not.
For a TRIM-enabled SSD, it will be pretty harder to recover data from it because the TRIM command immediately wipes off the deleted/lost file and makes the space empty.
Yes, It is possible to recover data from a dead or unrecognized SSD. All you need is a professional SSD recovery tool like Remo Recover to perform a hassle-free recovery from your dead or unrecognized hard drive.
Follow the below simple steps to start recovering data from a dead and unrecognized SSD.
1.) Download and install the Remo Recover tool on a working computer.
2.) Connect the dead or unrecognized SSD to the computer via a Card reader or USB Port.
3.) Now, Launch the software on your system, select the SSD and click on Scan.
4.) After completion of the scanning process, a list of recovered files is displayed under the Lost and Found folder or Lost Partition folder.
5.) You can preview all the recovered files from your dead SSD using the Preview feature for free.
6.) If you are satisfied with the recovery results, select the files which you want to restore and hit the Recover button to save them at your desired location.
To recover data from SSD on Mac all you have to do is download and install the Mac version of the Remo Recover tool which is Remo Recover Mac on your macOS computer and, follow the on-screen instructions of the tool to perform the recovery process.
You can also read the article recover data from Mac SSD to perform a hassle-free recovery process from SSD on macOS computers.